Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- MSA
- StringBuilder
- 재정의
- Test
- jwt
- 조합
- cache
- 생성자 주입
- DI
- lambda
- 필드 주입
- VUE
- KEVISS
- stream
- select_type
- hashcode
- redis
- DDL
- static
- docker
- jpa
- equals
- AOP
- 인덱스
- Spring
- Exception
- 열 속성
- SQL
- java
- 테스트 코드
Archives
- Today
- Total
백엔드 개발자 블로그
DB 트래픽 분산 본문
DB 트래픽을 왜 분산시키는 이유
- 데이터베이스의 더 많은 가용성을 확보하기 위함이다
- 더 많은 I/O 작업을 수행하기 위함이다.
- I/O작업이 많으면 메모리가 가득 찰수도 있고, 커넥션 풀이 부족할 수도 있고, 물리적인 디스크 용량이 가득찰 수 있다
DB I/O 가용성 확보 방법
1. DB 서버 스펙을 향상
실제로 많은 비용이 발생할 수 있다
2. 샤딩으로 데이터를 분산처리
샤딩으로 데이터를 분산처리하고 사용하는 과정은 그리 간단하지는 않다
3. 서비스에 따라 데이터베이스를 독립적으로 분리
MSA만 가능한 방법이다.
4. CQRS 패턴을 적용해서 Query용 데이터베이스와 Command용 데이터베이스를 분리
- Command 용으로는 성능을 최대한 올리는 있는 NoSQL을 사용한다.
- Query용으로는 연관관계를 좀 더 효율적으로 표현할 수 있도록 RDMS를 사용한다.
- 그리고 서로 다른 두 데이터베이스는 메시지 큐를 통해서 동기화 작업을 이뤄지게 된다. 이 과정에서 비용이 많이 발생한다.
5. 트래픽 분산
주어진 환경에서 가장 적은 비용으로 데이터베이스의 가용성을 확보할 수 있는 방법이다.
데이터베이스는 어떻게 분리하지?
- 백업용 또는 장애 복구용도로 SLAVE 데이터베이스를 두어 replication 과정을 거쳐 데이터가 SLAVE에 복제하게 된다
- 대부분 데이터베이스는 MASTER, SLAVE 구조로 운영되고 서비스 범위에 따라서 SLAVE를 여러개 두는 경우도 있다
그럼 읽기와 쓰기는 어떤 DB를 사용해야지?
- SLAVE 데이터베이스는 replication되어 단방향으로 데이터가 복제되기 때문에 직접 WRITE를 하게되면 MASTER 데이터베이스와 데이터 정합성이 깨지게 된다
- 그러므로 쓰기는 MASTER 데이터베이스를 사용하고, 읽기는 SLAVE 데이터베이스를 사용하면 된다
분산처리는 어떻게 하지?
- 동적으로 DataSource를 변경하면 된다.
MyBatis 기준으로 이야기해보겠다
일반적인 DataSource를 통해서 쿼리를 수행하는 과정

- sqlSessionTemplate은 PlatformTransactionManager를 사용한다
- PlatformTransactionManager는 인터페이스로 실제로 사용하는 구현 객체는DataSourceTransactionManager를 사용한다
- 별도로 재정의하지 않는다면 기본적인 DataSourceTransactionManager를 사용하게 되고 DataSourceTransactionManager는 DataSource Bean을 사용하게 된다
그럼 동적으로 DataSource를 변경하려면 어떻게 해야할까?

- 트랜잭션 수행시 동적으로 Datasource를 정의하기 위해서는 PlatformTransactionManager를 재정의해야 한다
@Bean(name = "transactionManager")
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("routingLazyDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return transactionManager;
}
- 재정의된 PlatformTransactionManager는 동적으로 DataSource를 할당할 수 있도록 LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy 객체를 사용한다
@Bean("routingLazyDataSource")
public DataSource routingLazyDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
return new LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}- LazyConnectionDataSourceProxy에 정의된 dataSource는 AbstractRoutingDataSource를 상속받은 객체로 determineCurrentLookupKey를 오버라이드하게 되면 동적으로 할당된 dataSource 시점을 지정할 수 있다
public DataSource getMasterDataSource() {
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties = new DataSourceProperties();
dataSourceProperties.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSourceProperties.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/temp");
dataSourceProperties.setUsername("root");
dataSourceProperties.setPassword("password");
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
private DataSource getSlaveDataSource() {
DataSourceProperties dataSourceProperties = new DataSourceProperties();
dataSourceProperties.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSourceProperties.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3307/temp");
dataSourceProperties.setUsername("root");
dataSourceProperties.setPassword("password");
return dataSourceProperties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().type(HikariDataSource.class).build();
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put("master", getMasterDataSource());
targetDataSources.put("slave", getSlaveDataSource());
CustomRoutingDataSource dataSource = new CustomRoutingDataSource();
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(getMasterDataSource());
return dataSource;
}
- AbstractRoutingDataSource는 targetDataSource를 결정할 수 있는 객체이다
- 구체적으로는 AbstractRoutingDataSource 객체에서 connection을 가져올때 어느 데이터소스를 가져올지 determineCurrentLookupKey() 메서드를 호출해서 결정한다
// AbstractRoutingDataSource.class
// 데이터 커넥션을 호출하는 메서드
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
}
// 데이터 커넥션을 호출하는 메서드
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
}
// 데이터 커넥션 호출하는 과정에서 DataSource 정보를 가져오는 로직
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
// determineCurrentLookupKey() 메서드를 호출해서 동적으로 분기처리할 DataSource를 구분해준다
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
}
return dataSource;
}
- 커스텀 데이터 소스 determineCurrentLookupKey
- 트랜잭션이 readOnly = true일 경우, “slave”키를 통해서 slave 전용 DataSource를 선택하게 한다
// CustomRoutingDataSource.java public class CustomRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { boolean currentTransactionReadOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly(); return currentTransactionReadOnly ? "slave" : "master"; } }
실습
- 두개의 쿼리를 호출해 볼 예정이다
@GetMapping("master")
public String testMasterDataSource() {
return stockApplicationService.testMasterDataSource();
}
@GetMapping("slave")
public String testSlaveDataSource() {
return stockApplicationService.testSlaveDataSource();
}- 하나는
readonly = true를 사용하고, 하나는readonly = false를 사용한다
// StockApplicationService.java
@Transactional(readOnly = false)
public String testMasterDataSource() {
return stockService.test("1");
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public String testSlaveDataSource() {
return stockService.test("1");
}
// StockService.java
public String test(String stockCodeName) {
StockDetail stockDetail = stockRepository.getDetailByStockCode(stockCodeName);
return stockDetail.getStockName();
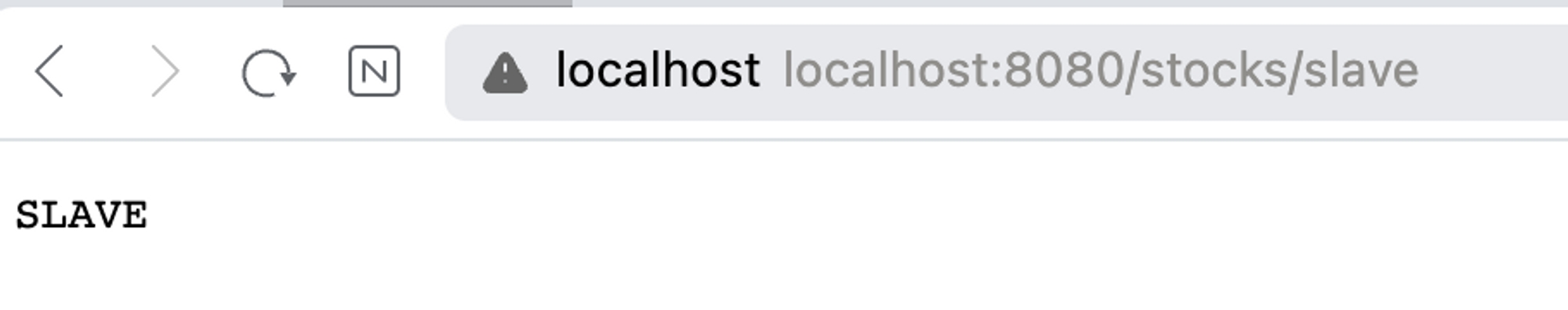
}- 데이터베이스는 두개를 준비하였다
- 동일한 스키마의 테이블에 stock_name 값에 디비에 따라서 다른 값을 저장해두었다
- master DB ⇒ stock_name = “master”
- slave DB ⇒ stock_name = “SLAVE”

- 우리가 기대하는 값은 트랜잭션이 read only가 false일 경우에는 MASTER DB를 바라보게 되고, true일 경우에는 SLAVE DB를 바라보게 된다
- 그럼 API를 호출해보자
- 마스터

- 슬레이브
참고
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| @Transactional (0) | 2024.05.13 |
|---|---|
| OSIV (0) | 2024.05.11 |
| Redisson trylock 내부로직 (0) | 2024.05.11 |
| RestTemplate 사용시 주의사항 (0) | 2024.05.09 |
| AOP 사용법 (0) | 2023.12.16 |


